Advanced Solutions
for Advanced Pathology
IgG (Polyclonal)
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
Cat. No. Description
Volume
45219 IMPATH IgG RTU R (Poly)
50 Tests
44318 IgG RTU R (Poly)
7 ml Ready To Use
44658 IgG 0,1 R (Poly)
100 µl liquid Concentrated
44659 IgG 1 R (Poly)
1 ml liquid Concentrated
Product Specifications
Designation
IVD
Reactivity
Paraffin
Visualization
Cytoplasmic
Control
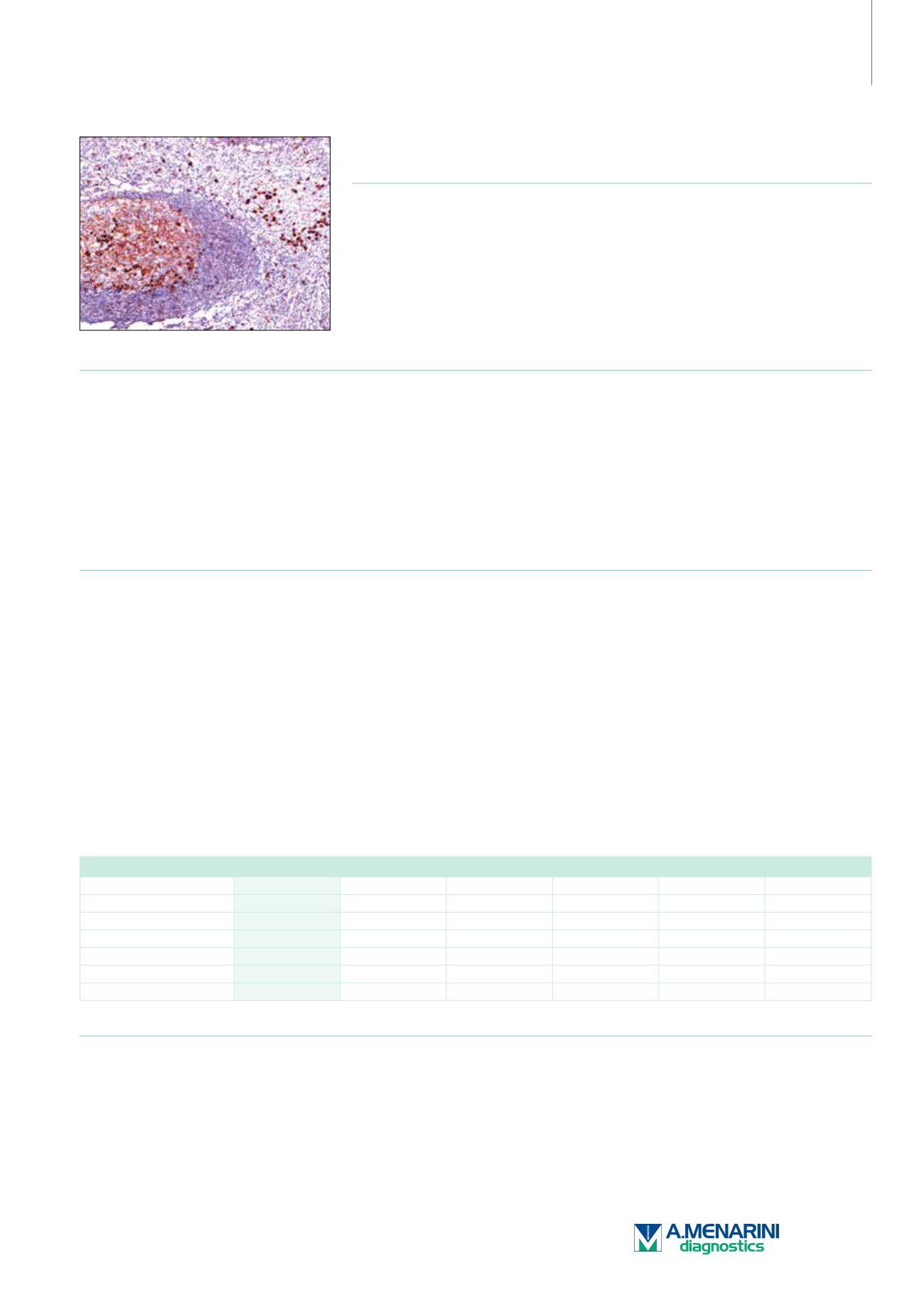
Tonsil
Stability
Up to 36 mo. at 2-8°C
Manual Protocol*
• Pretreatment: Heat Induced Epitope
Retrieval (HIER)
• Primary Antibody Incubation Time:
10-30min @ 25-37°C
• 2-step polymer detection
*Please refer to product insert for complete protocol.
ImPath Protocol*
• Dewax: Dewax Solution 2 (DS2)
• Pretreatment: Retrieval Solution pH 9.0
(TR1) 32min @ 98-103°C
• Primary Antibody Incubation Time:
10-90min @ 25-37°C
• HRP Polymer (Universal) or AP Polymer
(Universal) for 12 min
*Please refer to product insert for complete protocol.
Product Description
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a monomeric immunoglobulin, built of two heavy chains (γ) and two light chains. Each IgG has two antigen binding
sites. It is the most abundant immunoglobulin and is approximately equally distributed in blood and in tissue liquids, constituting 75% of
serum immunoglobulins in humans. IgG molecules are synthesized and secreted by plasma cells and B-cells. IgG antibodies are predominately
involved in the secondary antibody response, (the main antibody involved in primary response is IgM) which occurs approximately one month
following antigen recognition, thus the presence of specific IgG generally corresponds to maturation of the antibody response. Pro-inflammatory
cytokines, particularly IL-4 and IL-2, have a crucial role in activation of the IgG antibody response. This is the only isotype that can pass through
the human placenta, thereby providing protection to the fetus in utero. Along with IgA secreted in the breast milk, residual IgG absorbed through
the placenta provides the neonate with humoral immunity before its own immune system develops.
IgG can bind to many kinds of pathogens (for example viruses, bacteria, and fungi), and protects the body against such agents by agglutination
and immobilization, complement activation (classical pathway), opsonization for phagocytosis and neutralization of their toxins. It also plays an
important role in antibody-dependent, cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). IgG is also associated with type II and type III hypersensitivity.
Anti-IgG reacts with surface immunoglobulin IgG gamma chains. This antibody is useful when identifying leukemias, plasmacytomas, and B-cell
lineage-derived Hodgkin lymphomas.
Immunoglobulin, Heavy and Light Chain
IgG
IgA
IgD
IgM
Kappa
Lambda
Secretory Meningioma
-
+
-
+
Cutaneous Lymphoma
-
-
-
-
+/-
-/+
Myeloma
+
+
-/+
-/+
+/-
-/+
Diffuse LBCL
+
-
-
+
+/-
-/+
Marginal Zone Lymphoma
-
-
-/+
+
+/-
-/+
SLL/CLL
-
-
+
+
+/-
-/+
Reference
1. Arnold A, et al. New Eng J Med. 1983; 309:1593-1599.
2. Leong AS, et al. Manual of Diagnostic Antibodies for Immunohistology. Geenwich Medical Media Ltd. 1999. pp 217-219.
3. Hertel BF, et al. New Eng J Med. 1980; 302:1293-1297.
4. Taylor CR. Arch Path Lab Med. 1978; 102:113-121.
5. Warnake R, et al. Masson Publishing USA. 1981. pp 203-221.
6. Ando K, et al. Intern Med. 2000 Feb; 39(2):170-5.
7. Schmid U, et al. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995 Jan; 19(1):12-20.
147


